What Is a Low Voltage Contractor
Role and Importance of Low Voltage Contractor in Modern Infrastructure
A low-voltage contractor is pivotal in modern infrastructure, specializing in systems that operate below 50 volts AC or 120 volts DC. Their expertise spans various critical domains, including communication and security systems. They ensure efficient operation, safety, and compliance across diverse residential, commercial, and industrial settings.

Communication Systems
Communication systems are one of the primary areas of expertise for low-voltage contractors. These systems facilitate efficient data transmission and communication in today’s interconnected world. Low voltage contractors excel in the installation and maintenance of:
Telephone Networks: They design and deploy telephone systems that enable reliable voice communication, which is crucial for personal and business interactions. Contractors ensure that telephone networks are scalable and equipped with features like voicemail and call forwarding to meet diverse client needs.
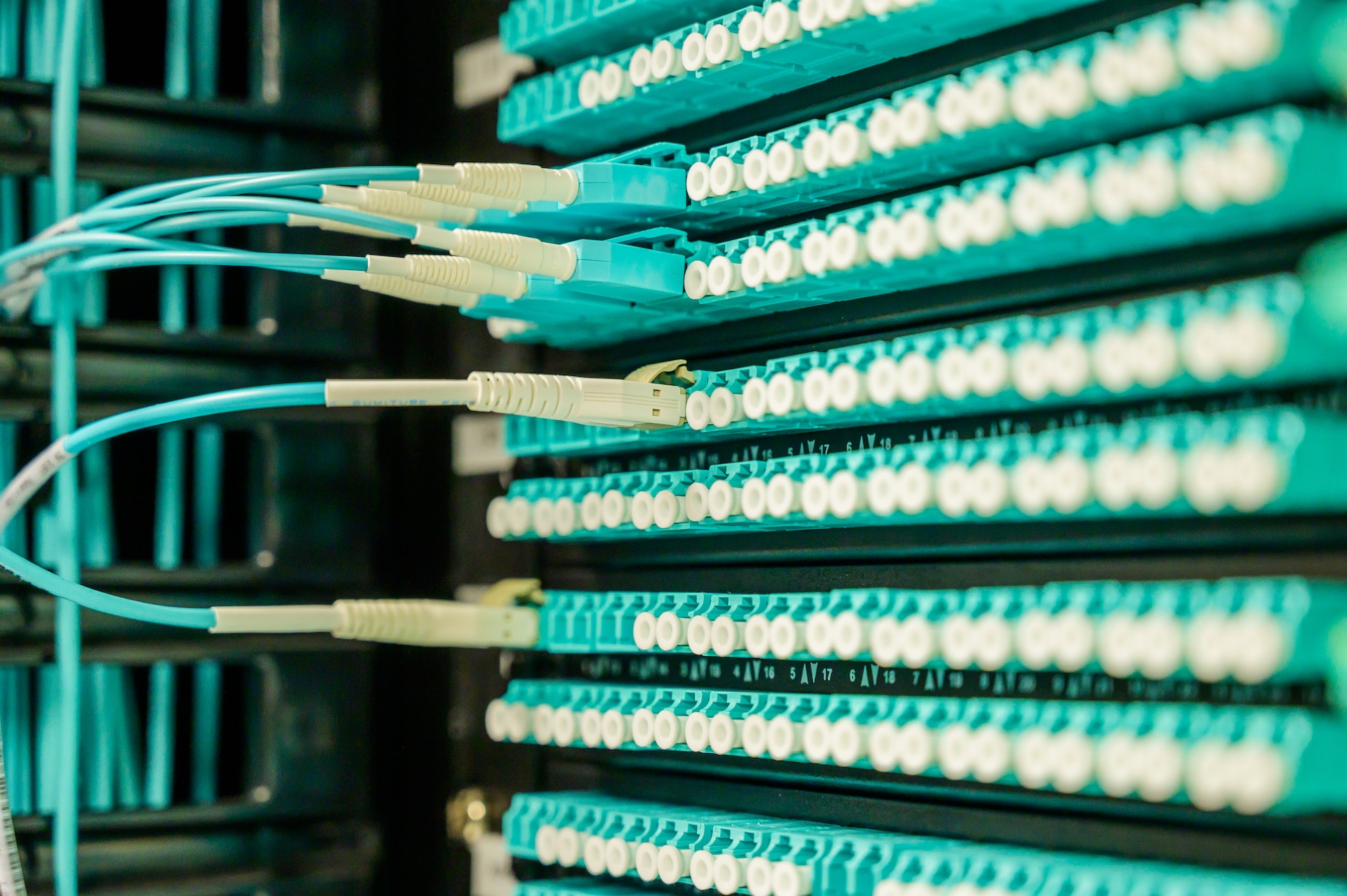
Data Cabling (Ethernet): Low voltage contractors are proficient in installing structured cabling systems, such as Ethernet, which form the backbone of local area networks (LANs). They carefully plan and implement cabling layouts to optimize data transfer rates and minimize signal interference, ensuring high-speed connectivity for computers, printers, and other networked devices.
Fiber Optic Installations: Low-voltage contractors specialize in fiber optic installations for high-speed data transmission. They deploy fiber optic cables capable of carrying large volumes of data over long distances with minimal signal degradation. Fiber optics are integral to modern telecommunications infrastructure, supporting internet access, video streaming, and teleconferencing services.
Contractors ensure these communication systems are installed securely and reliably to meet their clients’ communication needs. They conduct thorough testing and verification to ensure adherence to industry standards and regulatory requirements, providing clients with robust and scalable communication solutions.
Security Systems
Another critical responsibility of low-voltage contractors is the installation and maintenance of security systems. These low-voltage security systems protect properties, assets, and occupants by detecting and deterring unauthorized access, intrusions, and emergencies. Key components include:
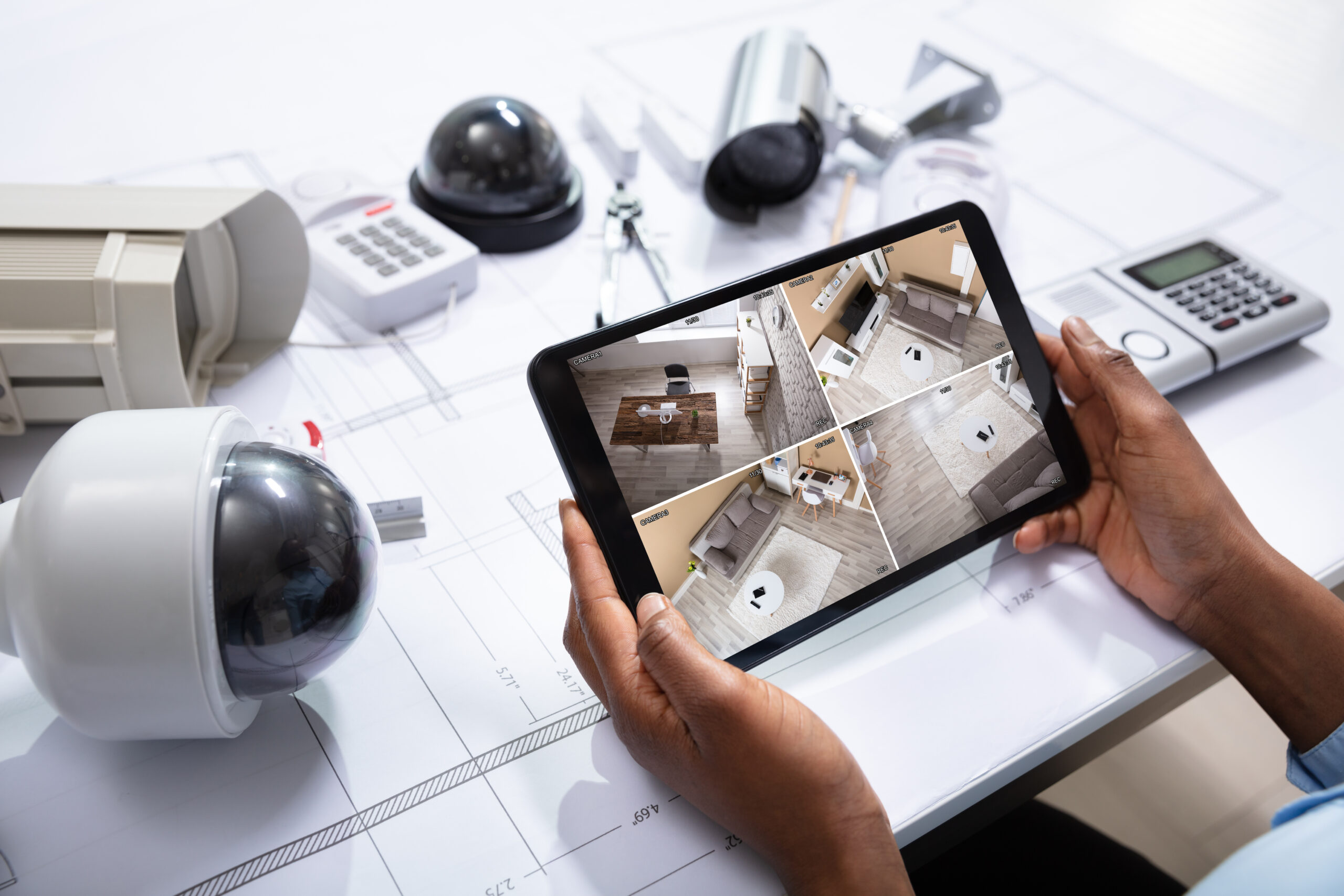
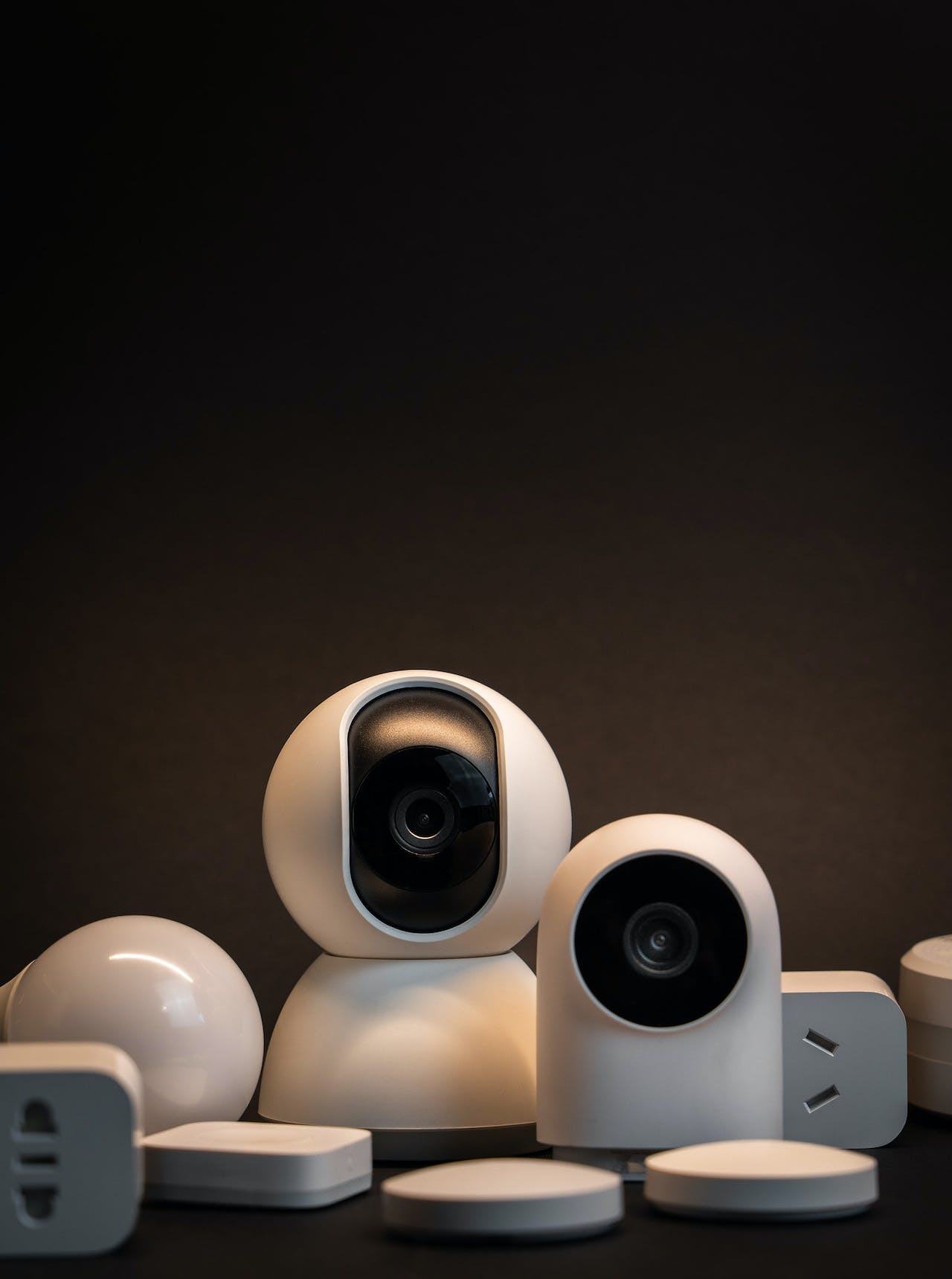
Surveillance Cameras: Low voltage contractors deploy surveillance systems comprising cameras strategically positioned to monitor critical areas of buildings and grounds. They integrate cameras with digital video recorders (DVRs) or network video recorders (NVRs) to capture and store footage for later review or evidence purposes.
Burglar Alarms: Contractors install burglar alarm systems with sensors that detect unauthorized entry attempts, triggering audible alarms and alerting designated personnel or authorities. They configure alarm systems to include motion sensors, door/window contacts, and glass break detectors for comprehensive security coverage.
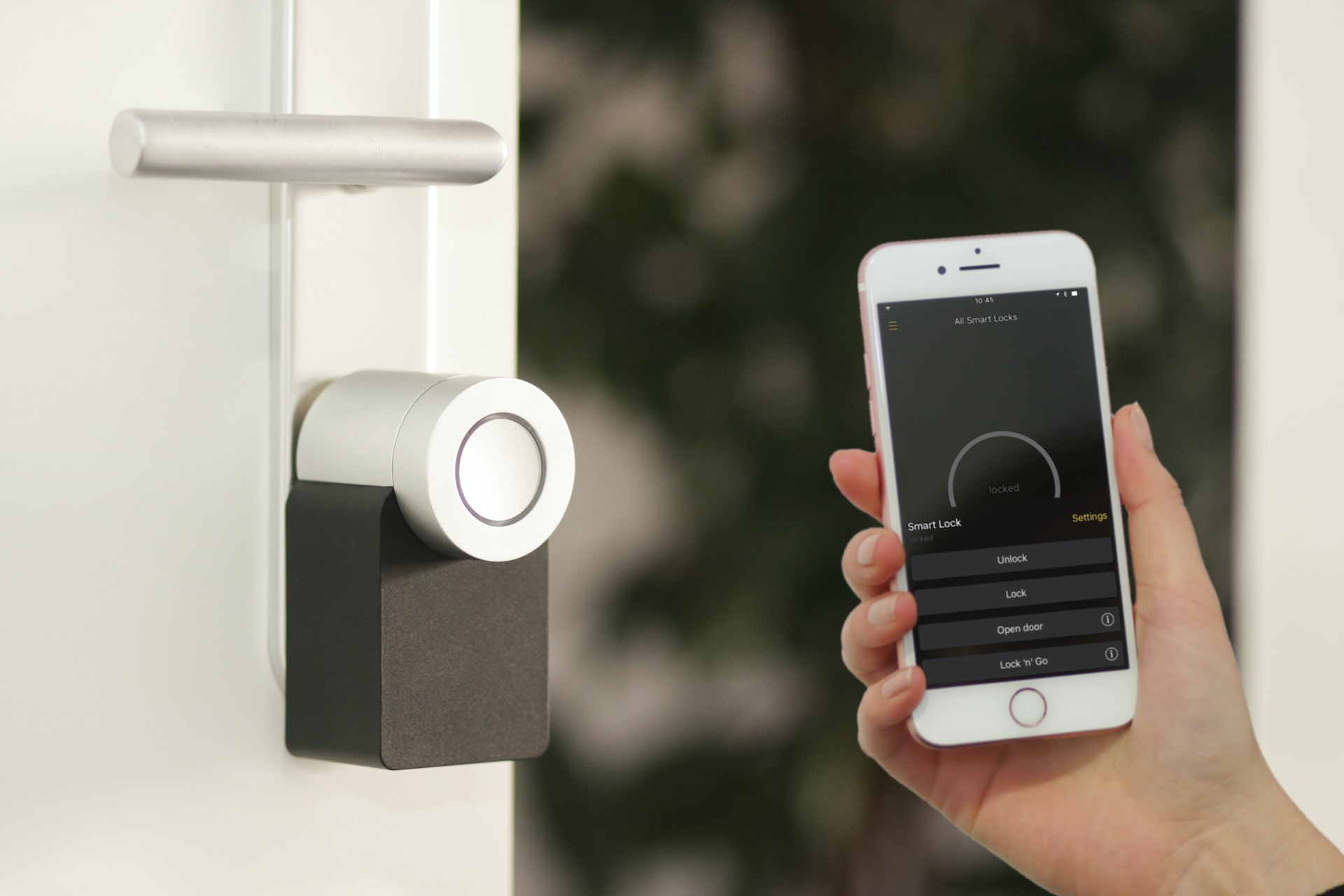
Access Control Systems: Low voltage contractors implement access control solutions that regulate entry and exit to buildings or specific areas within them. These systems utilize proximity cards, biometric readers, or keypad entry systems to authenticate individuals and manage access permissions based on predefined rules.
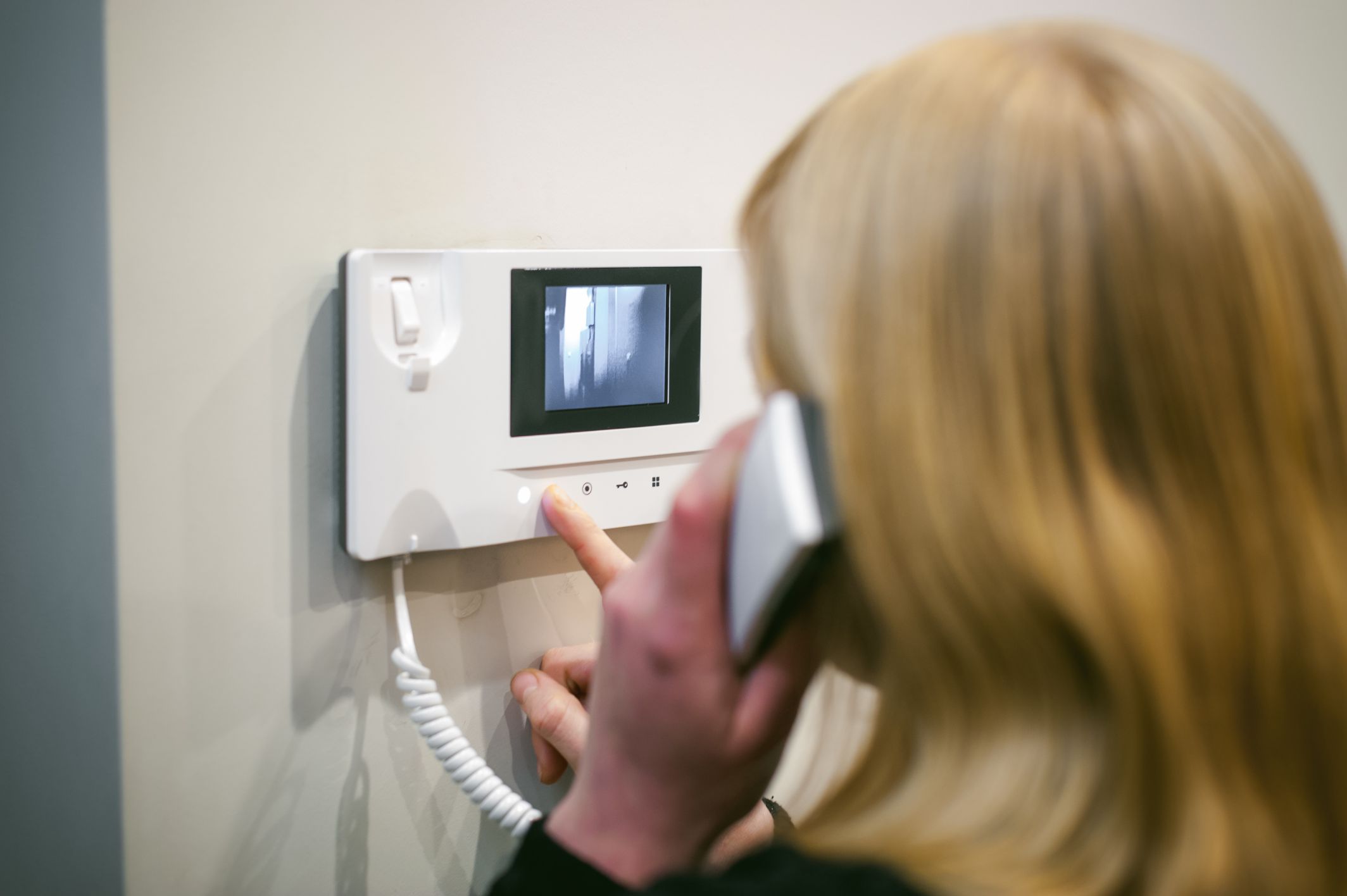
Intercoms: Communication during emergencies is facilitated through intercom systems installed by contractors. Intercoms allow two-way audio communication between different building areas, enabling rapid response coordination and communication with building occupants.
Expertise and Integration
Low-voltage contractor brings specialized knowledge and skills, enabling them to design, install, and maintain complex systems that meet specific client requirements and comply with industry standards. They collaborate closely with architects, engineers, and other construction professionals to integrate their systems seamlessly into larger projects.
Design and Planning: Contractors begin by assessing client needs and conducting site surveys to gather pertinent information for system design. They develop detailed plans that specify equipment requirements, installation procedures, and integration strategies to ensure compatibility and functionality. Installation and Deployment: With meticulous attention to detail, contractors execute system installations according to established plans and timelines. They coordinate equipment delivery, manage installation crews, and oversee wiring, mounting, and configuration processes to achieve optimal system performance.
Testing and Commissioning: Contractors conduct rigorous testing and commissioning procedures to verify system functionality and performance after installation. They simulate operational scenarios, conduct sensor sensitivity tests, and validate communication pathways to ensure reliable operation under normal and emergency conditions.
Training and Support: Low-voltage contractors provide comprehensive training to end-users, building occupants, and maintenance staff on system operation, emergency procedures, and routine maintenance tasks. They equip clients with the knowledge and skills to maximize system effectiveness and respond effectively to security incidents or communication challenges.
Maintenance and Upkeep: Beyond installation, contractors offer ongoing maintenance and support services to preserve system integrity and performance over time. They perform routine inspections, software updates, and preventive maintenance tasks to identify and rectify potential issues before they impact system reliability or compliance.
Compliance and Regulations: Low-voltage contractors adhere to stringent regulatory requirements and industry standards throughout the project lifecycle. They stay abreast of evolving regulations, codes, and best practices to ensure that installed systems meet or exceed safety, security, and operational guidelines.
Conclusion
In conclusion, low-voltage contractors contribute to modern infrastructure, specializing in communication and security systems that enhance safety, efficiency, and connectivity across diverse environments. Through their expertise in designing, installing, and maintaining systems that operate below 50 volts AC or 120 volts DC, contractors ensure robust communication networks, comprehensive security measures, and seamless integration into larger construction projects. Low-voltage contractors play a vital role in shaping safer, more secure, technologically advanced built environments by prioritizing client needs, regulatory compliance, and system reliability.

Quality Assurance and Maintenance
Beyond installation, low-voltage contractors are responsible for ongoing maintenance and support. They conduct regular inspections, troubleshoot issues, and perform necessary repairs to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the systems they install. This proactive approach helps prevent downtime and ensures clients can rely on their systems for years.
Audiovisual Systems and Environmental Controls by Low Voltage Contractor
Low-voltage contractors are instrumental in installing and maintaining crucial systems such as audiovisual setups and environmental controls. These specialists handle tasks ranging from setting up audio systems to maintaining HVAC controls, ensuring optimal functionality and efficiency across various settings.
Audiovisual Systems
Low-voltage contractors excel in deploying and servicing audiovisual systems integral to modern communication and entertainment environments. They specialize in installing and maintaining audio systems, facilitating precise sound reproduction for diverse applications. It includes configuring equipment for public address systems, concert venues, and educational institutions, ensuring high-quality sound delivery that meets specific client needs.
Moreover, these contractors are adept at managing video conferencing equipment, which is crucial for remote communication in business settings. They ensure seamless integration of cameras, microphones, and displays to facilitate effective virtual meetings and collaborations. Low-voltage contractors optimize video conferencing setups for enhanced connectivity and user experience by staying updated with technological advancements.
Additionally, low-voltage contractors cater to the installation and upkeep of home theater systems, providing homeowners with immersive entertainment experiences. From configuring surround sound systems to calibrating projectors and screens, they ensure optimal audio and visual performance in residential spaces. Their expertise extends to integrating smart home technologies, enabling seamless control of entertainment systems via mobile devices or voice commands.
Environmental Controls
Another vital area of expertise for low-voltage contractors is environmental control systems, particularly HVAC controls. They play a pivotal role in installing and maintaining heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems that regulate indoor climate conditions. These contractors optimize energy efficiency by implementing sophisticated controls and sensors while ensuring comfort and air quality within residential, commercial, and industrial buildings.
Low-voltage contractors use their technical proficiency to design HVAC systems tailored to specific building requirements. They assess heating and cooling demands, select appropriate equipment, and install ductwork and piping systems for optimal airflow distribution. Additionally, they integrate intelligent HVAC controls, enabling remote monitoring and adjustment of temperature settings to maximize energy savings and occupant comfort.
Furthermore, low-voltage contractors conduct regular inspections and preventive maintenance to uphold HVAC system performance. They perform filter replacements, duct cleaning, and system recalibration tasks to mitigate potential issues and extend equipment lifespan. By offering responsive repair services, they promptly address malfunctions to minimize downtime and ensure the uninterrupted operation of environmental control systems.
Fire Alarm and Detection Systems: The Expertise of Low Voltage Contractor
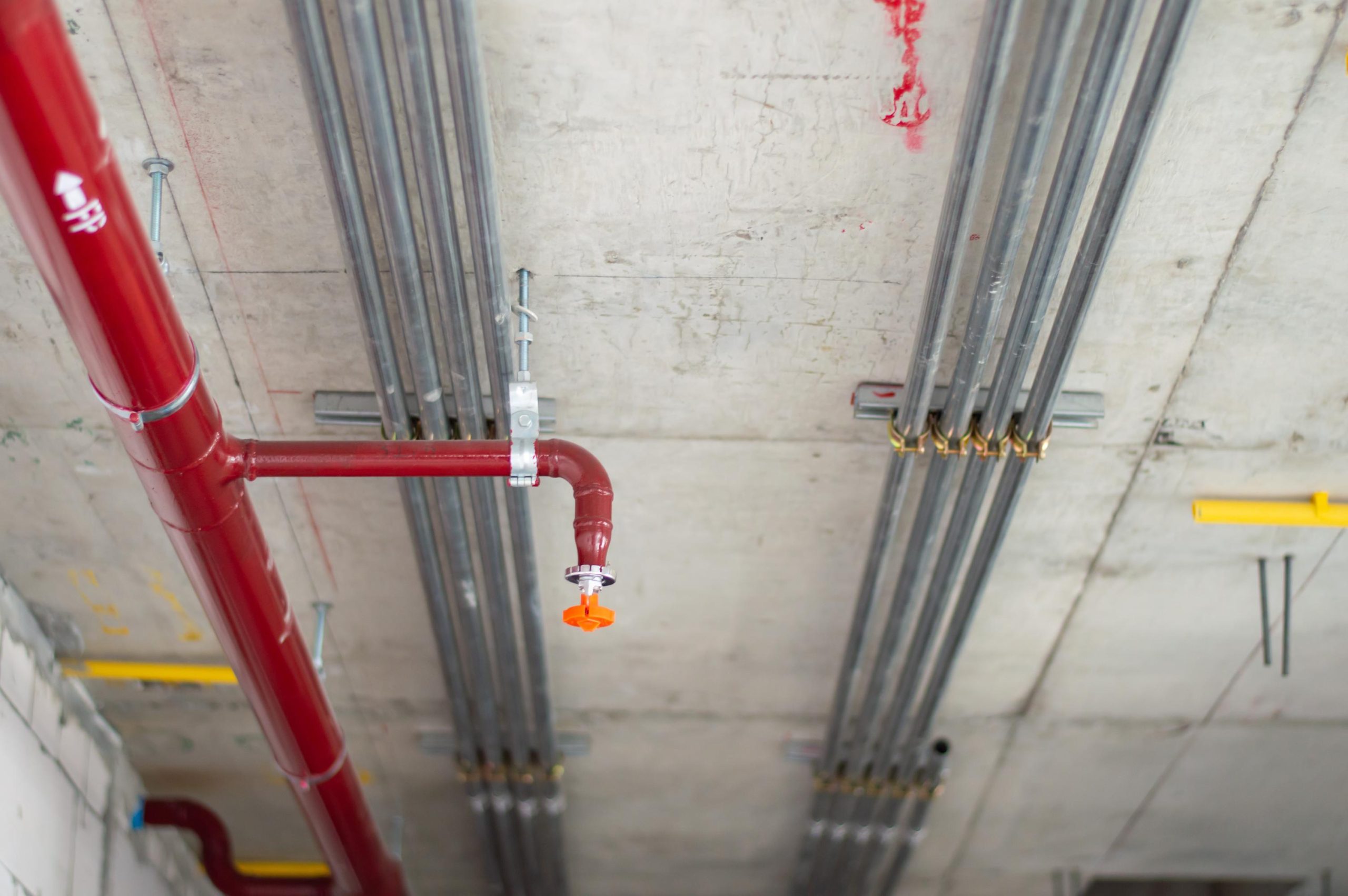
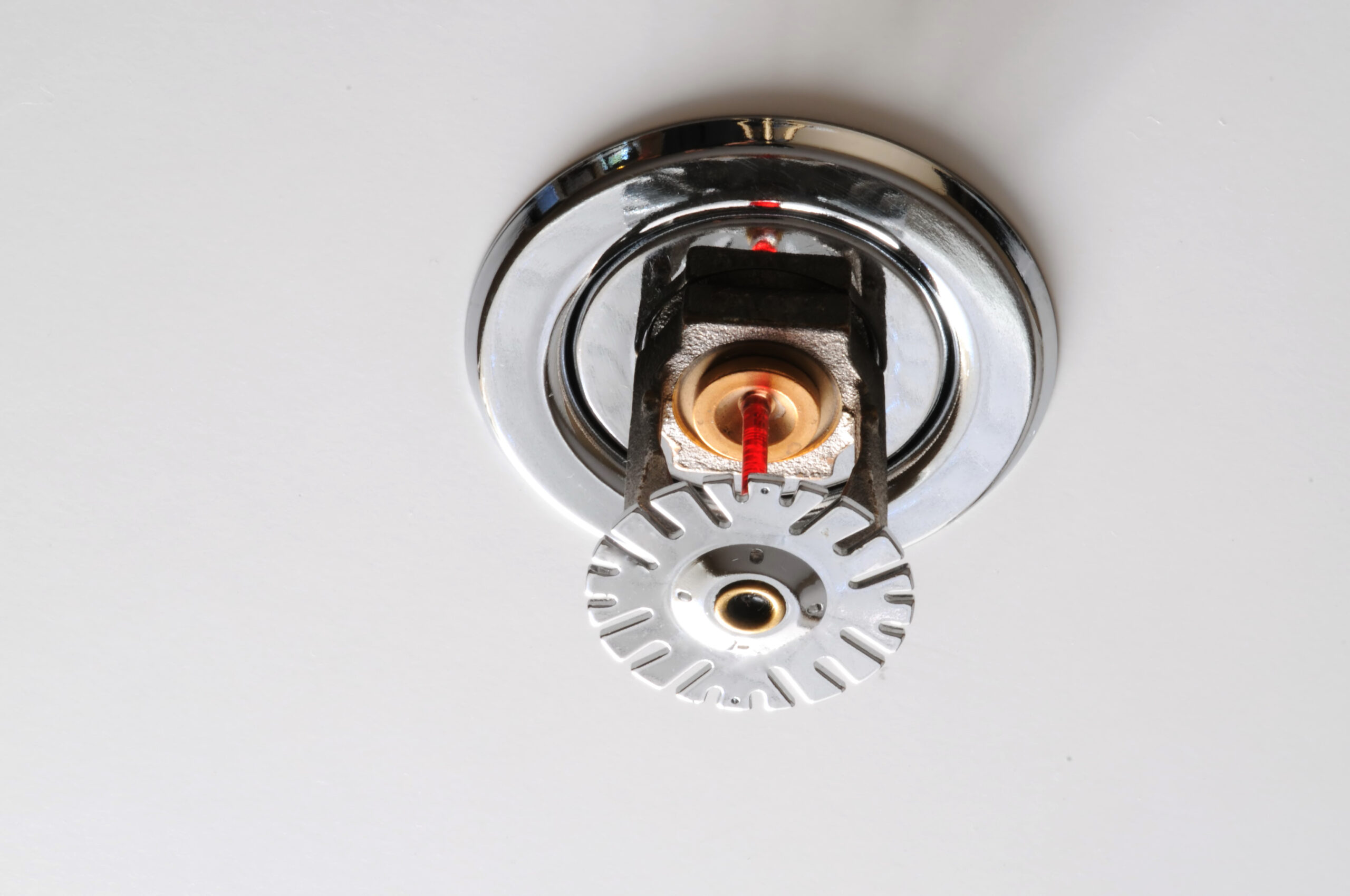
Low voltage contractors specialize in designing, installing, and maintaining critical fire alarm and detection systems. These systems are essential for safeguarding lives and property by providing early warning of fire emergencies. Low-voltage contractors ensure the reliability, functionality, and compliance of fire alarm systems, smoke detectors, and emergency lighting systems across various residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
Importance of Fire Alarm Systems
Fire alarm systems are fundamental safety components in buildings. They detect the presence of fire through smoke or heat sensors and alert occupants to evacuate promptly. Low-voltage contractors are responsible for designing these systems according to stringent codes and regulations to ensure comprehensive coverage and effective emergency operation.
The design phase involves assessing the building layout and occupancy requirements to determine optimal sensor placement and system configuration. Contractors select appropriate fire alarm control panels, detectors (such as smoke, heat, and flame detectors), notification devices (such as horns, strobes, and speakers), and initiating devices (such as manual pull stations). They integrate these components into a cohesive system that provides reliable detection and notification capabilities tailored to the building’s needs.
Installation Process
Once the design is finalized, low-voltage contractors install the fire alarm systems. It involves mounting detectors in strategic locations throughout the building, such as corridors, stairwells, and rooms with high fire risk. They also ensure proper wiring and connectivity between sensors, control panels, and notification devices to establish a robust communication network.
Emergency lighting systems are also installed to illuminate exit paths during power outages or fire emergencies, aiding safe evacuation. Low voltage contractors select and install emergency lights with battery backup, ensuring continuous operation when primary power sources fail. They verify compliance with local building codes and standards to guarantee that fire alarm and emergency lighting systems meet regulatory requirements and provide reliable performance under diverse conditions.

Integration with Building Infrastructure
Low-voltage contractor collaborates with architects, engineers, and other construction professionals to integrate fire alarm systems seamlessly into building infrastructure. They coordinate installation schedules and logistics to minimize disruption to ongoing construction activities while ensuring adherence to project timelines.
During integration, contractors conduct thorough testing and commissioning of fire alarm systems to verify functionality and performance. They simulate alarm activation scenarios to confirm proper sensor operation, alarm notification, and emergency response procedures. They provide comprehensive training to building occupants and maintenance personnel on system operation, evacuation protocols, and routine maintenance tasks to enhance safety awareness and readiness.
Routine Maintenance and Inspections
Beyond installation, low-voltage contractors are responsible for ongoing maintenance and periodic fire alarm and detection system inspections. They conduct routine tests, assessments, and preventive maintenance to identify and rectify potential issues before they compromise system performance.
Maintenance tasks include testing detectors for sensitivity, verifying communication pathways, inspecting wiring integrity, and checking battery backup systems. Contractors document maintenance activities and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and manufacturer recommendations to preserve system reliability and longevity.
Emergency Response and Support
Low-voltage contractors provide responsive support during system malfunctions or false alarms. They offer emergency repair services to address issues and restore system functionality promptly. Contractors collaborate with fire departments and emergency responders to facilitate swift and coordinated responses during fire emergencies, ensuring effective evacuation and mitigation of potential hazards.
Conclusion
In conclusion, low voltage contractors are critical in designing, installing, and maintaining fire alarm and detection systems for building fire safety. Their expertise ensures the reliable operation and compliance of fire alarm systems, smoke detectors, and emergency lighting systems, safeguarding lives and property. By delivering comprehensive services from system design to ongoing maintenance and emergency support, low-voltage contractors create safer environments and enhance preparedness for fire emergencies across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors.
Automation Systems: Enhancing Convenience and Efficiency
Low-voltage contractors specialize in implementing smart homes and building automation systems, revolutionizing how lights, appliances, and other devices are controlled in residential, commercial, and industrial environments. These systems leverage advanced technologies to enhance convenience, energy efficiency, and operational management.
Implementation of Smart Automation
Low-voltage contractor plays a pivotal role in designing and deploying automation solutions tailored to meet clients’ specific needs. They assess the infrastructure and requirements of homes or buildings to determine the optimal automation components and functionalities. It includes:
Lighting Control: Contractors install intelligent lighting systems that allow users to remotely control and automate lighting levels, schedules, and ambiance settings via mobile apps or voice commands. Automation optimizes energy consumption by dimming or turning off lights in unoccupied areas, reducing electricity costs and environmental impact.
Appliance Integration: Smart automation extends to appliances such as thermostats, HVAC systems, security cameras, and kitchen appliances. Contractors integrate these devices into centralized control systems, enabling users to monitor and adjust settings remotely for enhanced comfort, security, and operational efficiency.
Energy Management: Automation systems include energy monitoring and management features that provide real-time insights into energy usage patterns. Contractors implement intelligent meters and sensors to track electricity consumption. They also identify inefficiencies, and recommend adjustments to minimize waste and lower utility bills.
User Interface and Accessibility: Low-voltage contractor ensures intuitive user interfaces for seamless interaction with automation systems. They configure touch panels, mobile apps, or voice-activated assistants to simplify device control and programming. It empowers users to manage their environments effortlessly.
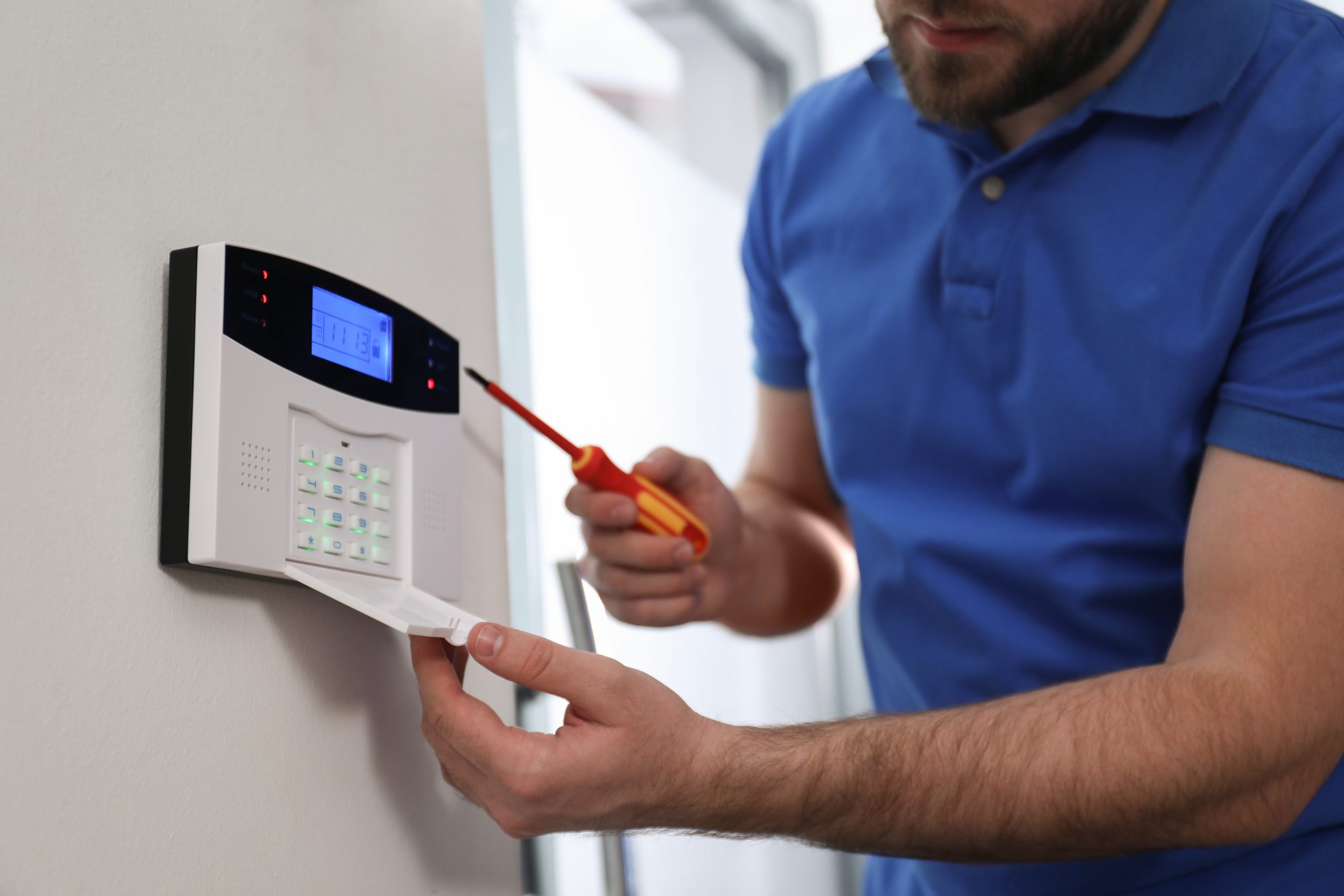
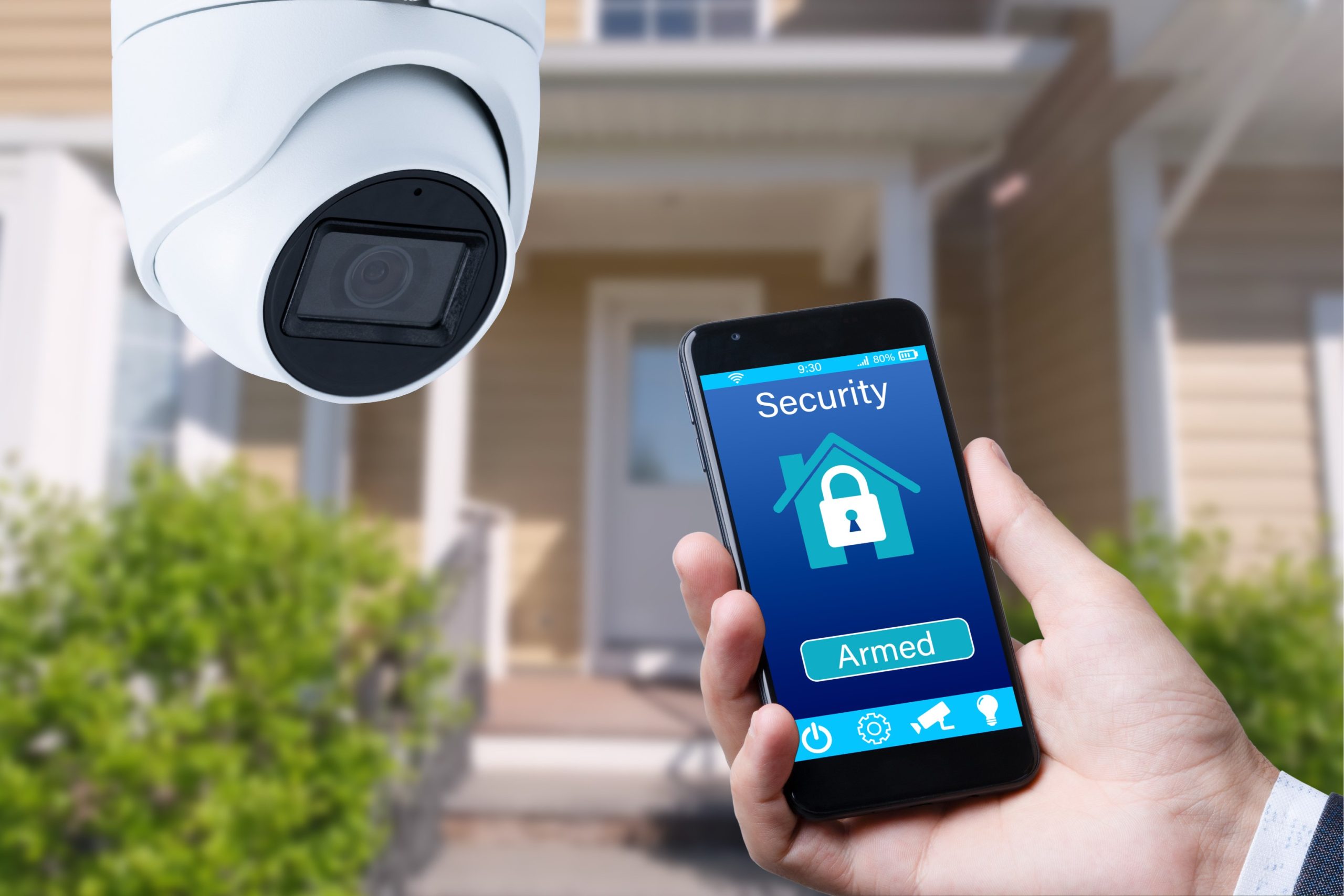





















 You can arm the alarm system once you’ve chosen the arming mode and entered your passcode. Press the designated button or enter a specific command on the keypad to initiate the process. Your system may provide an exit delay to allow you to leave the premises without triggering the alarm.
You can arm the alarm system once you’ve chosen the arming mode and entered your passcode. Press the designated button or enter a specific command on the keypad to initiate the process. Your system may provide an exit delay to allow you to leave the premises without triggering the alarm.

